Without Styrene, the world as we know it would be vastly different. The ability to isolate, or rather distill Styrene was an achievement in chemistry that became a catalyst for inventions that the modern world benefit from to this day.
Polystyrene and Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) would never have come into existence were it not for Styrene and its ability to be polymerize with so many different elements. The importance of Styrene can be seen all around us nearly every day of our lives.
According to the Styrene Information & Research Center, this importance has brought the annual Styrene sales to over 28 billion dollars, and places in the “100 most important chemical compounds”. Styrene is known by many other names including vinyl benzene, ethenylbenzene, phenylethylene, Styrol, Cinnamene, Diarex HF 77, and Styrolene. In natural forms, Styrene is found in hundreds of plants and substances in nature. Small amounts of Styrene naturally exist in many things that we eat and drink such as strawberries, coffee beans, peaches, wheat, cheese, cinnamon, wine, beer, and the balsamic tree just to name a few.
In the interest of being your source for information about Styrene and EPS, we have compiled the following information just for you. You may find it well worth the time and effort to learn since the impact of Styrene and expanded polystyrene have forever changed the way in which we live.
Styrene and Men of Science
Many of the scientists and pharmacists listed below were instrumental in Styrene research in its earliest days of experimentation. We cannot list all those that

Expanded Polystyrene
Expanded Polystyrene has been the proven answer to common packaging, insulative, and construction material solution for decades. It is unique in that it is a

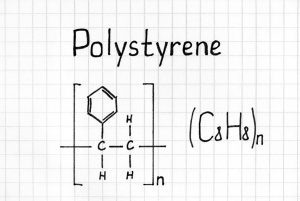
Polystyrene and Polymers
Simply put, Polystyrene is a synthetic polymerized thermoplastic resin using the Styrene monomer. It is known as a long-chain hydrocarbon. This stiffer type of Polystyrene

Styrene and How It’s Made
Styrene is a clear organic liquid hydrocarbon that is produced mainly from petroleum products after a process of fractional distillation to extract the olefins and aromatics
